‘Carbon footprint’ is a term that now widely refers to the amount of carbon emitted by an organization or activity. The carbon footprint makes up part of the overall Ecological Footprint as it is a competing demand for space that is biologically productive.
When the carbon footprint is assessed within the context of the total Ecological Footprint, the carbon dioxide emissions – in tonnes – are expressed as the total area of productive land required to negate those emissions. From there, the biocapacity necessary to neutralize emissions from fossil fuels can be calculated.
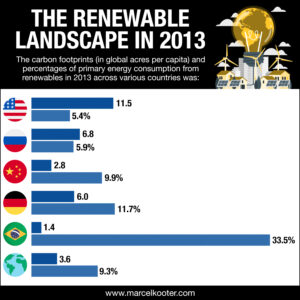
Senior business leaders in the field of renewable energy – such as Marcel Kooter, who has a strong focus on sustainable solutions – understand that reducing our carbon footprint is vital for humanity to live within the means of our planet.
How Is a Carbon Footprint Measured?
A carbon footprint can be calculated by conducting a GHG emissions assessment, a lifecycle assessment, or other means of carbon accounting. For an individual wanting to discover their personal carbon footprint, several free calculators exist to help establish this.
Calculating the carbon footprint of an industry, product or service is a complex undertaking. An LCA (Life-Cycle Assessment) is one tool that can be used to help calculate this, as is the deployment of the Greenhouse Gas Protocol for tracking emissions.
How to Reduce Personal Carbon Footprint
In July 2017 a study was published in the Environmental Research Letters scientific journal that found that the most significant way an individual can reduce their personal carbon footprint is to have one less child and to live car-free.
Dietary choice can also have a major impact on carbon footprint. Scientists at the University of Chicago suggest that replacing just one third of the animal protein found in the average American’s diet with plant protein could reduce the individual’s carbon footprint by half a tonne. Cutting back on food waste can also help reduce a person’s carbon footprint. Food waste and its associated carbon emissions adds to a household’s overall footprint, plus entails the release of additional emissions through the transporting of this waste to the garbage dump.
Cutting back on the use of heating and air conditioning in the home, installing insulation to the walls and attic of a property, and applying weather stripping or caulking to the areas around doors and windows can reduce heating costs by more than 25%.
Take a look at the embedded PDF for more information about the carbon footprint and the commitments made in the Paris Climate Agreement.

